Practice Test for Test 3 Unit 3 - Answers
Use the following information to answer questions 1
and 2.
Codon on mRNA (5’ŕ3’) and corresponding amino
acid
UUA leucine AAG lysine UAA stop UGC cysteine
GCA alanine GUU valine AAU asparagine UCG,
UCU serine
1. The anticodon (5’ŕ3’) in tRNA for the amino
acid lysine is
a. CUU
b. GAA
c. TTC
d. UUC
2. If a strand of mRNA reads
5’ AAU GUU AAG 3’, the amino acid sequence would be
a. asparagine-valine-lysine
b. asparagine-alanine-stop
c. asparagine-valine-asparagine
d. leucine-lysine-serine
3. The best definition of
"expression" is:
a.
both transcription and translation of a gene
b. the binding of DNA
polymerase to the lagging strand
c. translating RNA code into
protein code
d. uptake of naked DNA into
a cell
4. Constitutive genes:
a. are always expressed
b. are regulated to conserve
energy
c. are structural
d. encode repressor proteins
5. An operon is a:
a.
group of coordinately regulated genes with related functions
b. group of three
nucleotides in mRNA
c. nucleotide sequence in
DNA where the RNA polymerase binds
d. nucleotide sequence in
RNA that allows the RNA polymerase to proceed down the gene
6. According to the lac operon model, for the synthesis of b-galactosidase to occur
a. lactose must bind to b-galactosidase
b. allolactose must bind to the repressor protein
c. the repressor protein must bind to the operator
site
d. the repressor protein
must not be synthesized
7. When a DNA strand is
being synthesized, a bond is formed between two adjacent nucleotides on the
same strand. This bond is called a:
a. hydrogen bond
b. lagging bond
c. ligation bond
d. phosphodiester bond
8. DNA replication is
referred to as “semiconservative” because the ds DNA following replication:
a. contains some RNA
nucleotides and some DNA nucleotides
b. is made by an enzyme
called DNA conservatase
c. is made up of 1 old strand and 1 new strand
d. is made up of 2 strands
running in opposite directions
9. Transformation is the transfer of DNA from a
donor to a recipient cell
a. as fragments of naked DNA
b. by a bacteriophage
c. by cell-to-cell contact
d. by sexual reproduction
10. A plasmid is a(n):
a. ampicillin sensitive strain of E. coli
b.
circular, self-replicating DNA molecule that can transmit genes from one
bacterium to another
c. eukaryote used in genetic engineering
d. piece of DNA stored in a
yeast cell
11. The bacterium Corynebacterium
diphtheria produces toxin and causes diphtheria only when it is
lysogenic. This means that C. diphtheria:
a. contains a plasmid that
carries the genes for diphtheria toxin
b. has been lysed by a
T-even phage
c. has undergone
transformation
d. is infected with a lysogenic bacteriophage
12. Animal viruses enter
host cells by what two mechanisms?
a. budding and lysis
b. endocytosis and blebbing
c. endocytosis and fusion
d. fission and fusion
13. All of the following
viruses belong to the Poxviridae EXCEPT:
a. chickenpox
b. cowpox
c. monkeypox
d. smallpox
14. All of the following
viruses have been associated with cancer EXCEPT:
a. Epstein-Barr Virus
(Herpesviridae)
b. Genital warts virus
(Papillomaviridae)
c. Hepatitis B virus
(Hepadnaviridae)
d.
Rhinovirus (Picornaviridae)
15. HIV belongs to the
family Retroviridae. What is a unique feature of the Retroviridae?
a. they are not found
outside central
b. they are transmitted by
animal bites
c.
they have an RNA genome that is copied to DNA
d. they are visible to the
unaided eye
16. Which of the following
RNA viruses evolved within the last 10 years?
a. poliovirus
b.
SARS-CoV
c. smallpox
d.
17. In the laboratory, you used pure cultures of Halobacterium
salinarium. This organism is a
___________ and as such, experiences a(n) ____________environment when placed
in distilled water.
a. halophile; hypotonic
b. psychrophile; isotonic
c. thermophile; hypertonic
d. thermophile; hypotonic
18. RFLPs
a. are fragments
of DNA
b. are genes
c. result from
digests with restriction enzymes
d.
a and c only
e. all of the
above
19. Restriction enzymes:
a. are important tools in the process of genetic
engineering
b. can not be exported to other countries, their
sale is restricted
c. recognize and cut DNA at specific sequences
d. a and c only
20. The procedure in which small amounts of DNA are
amplified is called ____________.
a. DNA Fingerprinting
b. gel electrophoresis
c. Polymerase Chain Reaction
(PCR)
d. restriction digest
21. All of the
following are necessary for PCR EXCEPT:
a. DNA
polymerase
b. GTP, CTP,
TTP, and ATP
c. Primers
d.
RNA polymerase
22. What structure
is specifically responsible for transporting genetic material from one
bacterium to another during conjugation?
a. sheath
b.
pili
c. capsid
d. all the above
23. pUC18 is a:
a. gene
b. plasmid
c. recombinant bacterium
d. strain of Escherichia coli
24. In the transformation laboratory, the agar
plates _______________ and growth indicated
_____________.
a. contained ampicillin; ability to grow in the
presence of this antibiotic
b. were selective; ampicillin resistance
c. were selective; successful transformation
d. all of the above
25. All of the following statements are true about
bacteriophages EXCEPT:
a. they are too small to be seen using a light
microscope
b. they replicate in young, actively growing
bacterial cells
c. they always kill their
host cell by lysing it
d. they can be detected by the presence of plaques
|
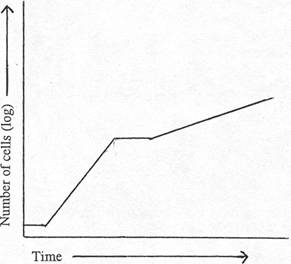
Use the following graph, which shows bacteria
growth in a medium that contains both glucose and lactose, but contains 10X
as much lactose as glucose, to answer questions 26 and 27.. |
|
26. During the first log phase, which carbohydrate
is being utilized? a. glucose b. lactose c. both glucose and lactose |
|
|
27. If the bacteria have been in log phase, why do
they go through a second log phase? a. the bacteria are dying b. the bacteria need to express genes for using
glucose c. the bacteria need to
express genes for using lactose d. the culture has accumulated waste products that
inhibit growth |